~ What is CNC Precision Machining? - A Guide By Rotec ~
CNC precision machining is where the processing of parts takes place to a very high tolerance, using a machine tool and a computer numerical control. It is an option that is common for many companies where there is a requirement for the production of millions of identical parts and components, a cost-effective solution when compared with manual machining.
What is CNC machining?
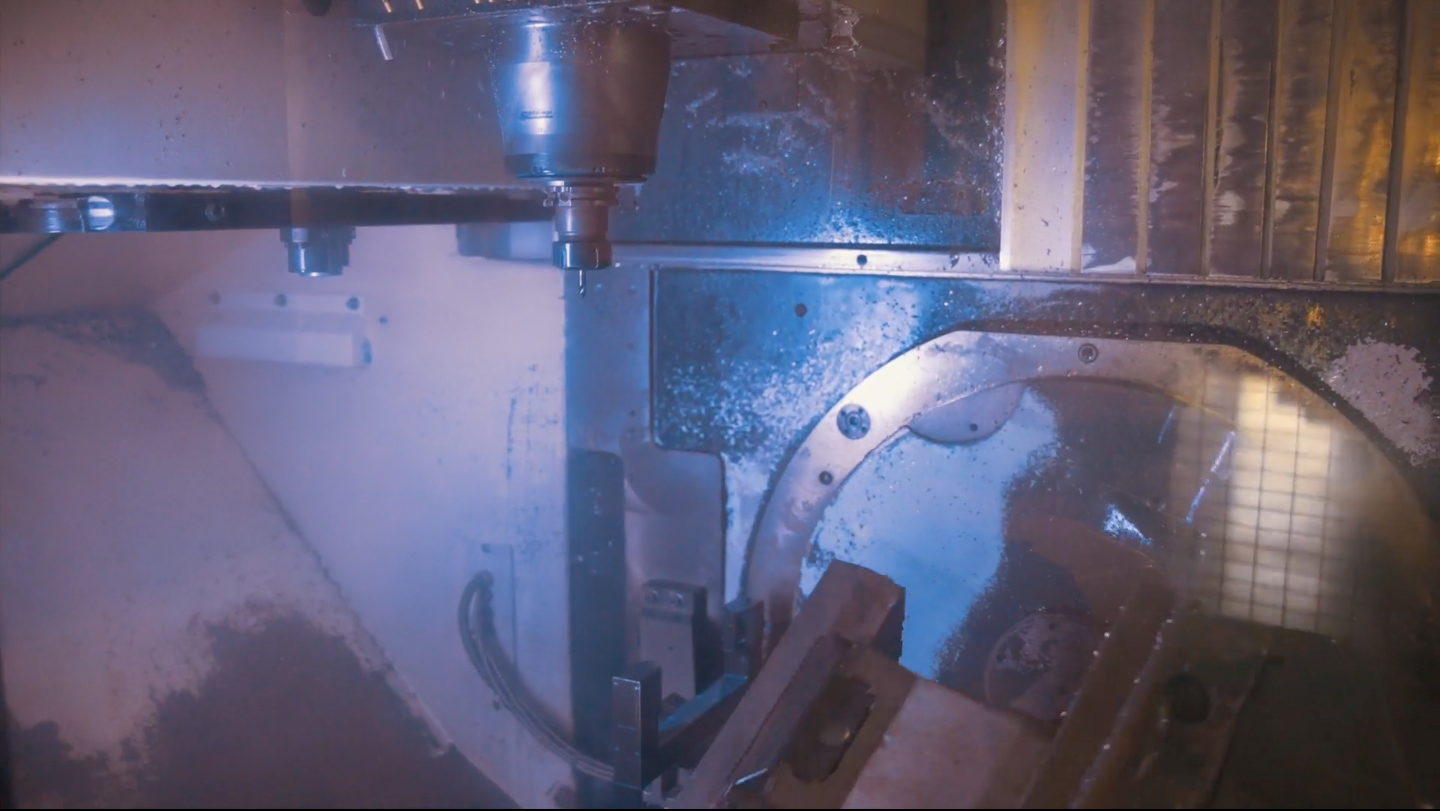
Precision machining with a CNC machine is simple. You set up a machine tool and provide it with the software commands that lets it know what is required. From these commands, the machine performs the process whilst the human element is overseeing remotely. The cutting process is put in place using computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturer (CAM) blueprints. These are crucial programmes, as they often contain detailed 3D outlines that allow for precision creation during the cutting process.
Practically, the materials involved are placed in a fixture or workpiece at the beginning of each cycle, ensuring that the part being worked on remains stationary throughout the cutting operation. Once the cutting has been completed for that cycle, the part is ejected from the machine and is ready for inspection or to put the finishing touches to it.
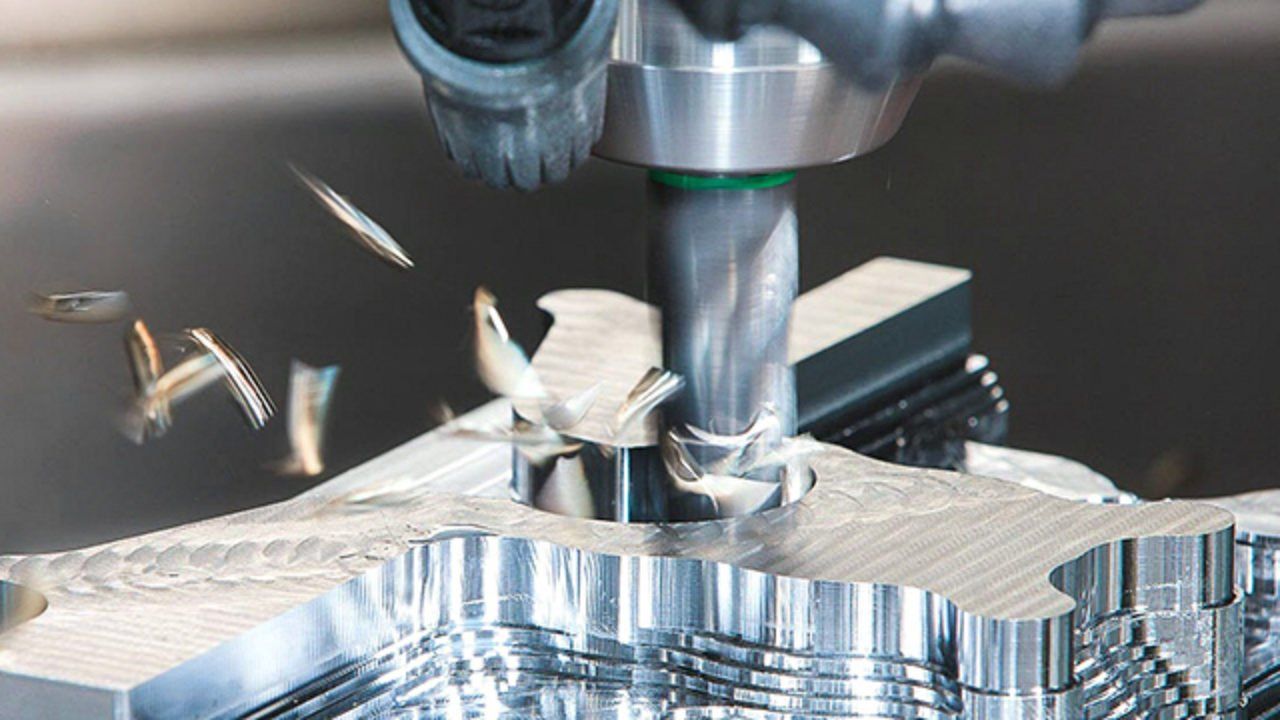
Using advanced machine tools within the process of precision machining helps to create the most interesting parts and complex geometries, with CNC tolerance standards typically seen at +/-0.005 inches but within CNC precision machining reaching tolerances of +/-0.002 inches to +/-0.0002 inches.
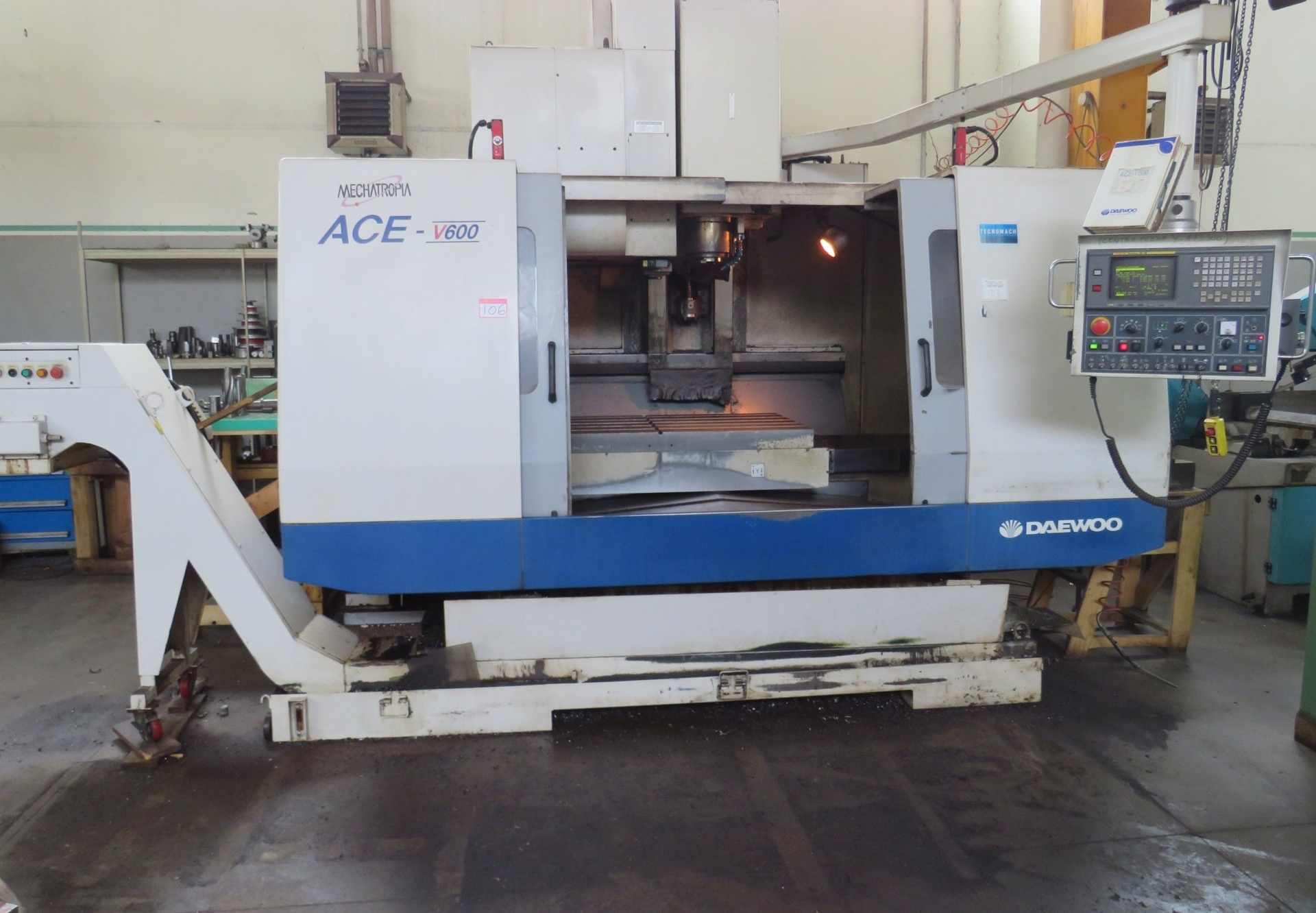
Types of precision CNC machine tools
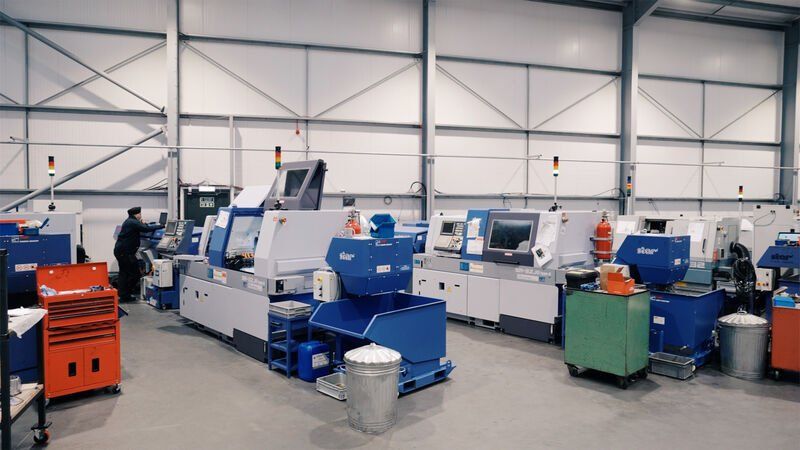
There are many different techniques, machines and tools that can be used to deliver quality parts and components. Each requires a different type of machining equipment for optimum results. In some cases, a finished piece might have required the use of multiple machines, whereas others might only need one CNC machine. Some of these include:
CNC milling – Characterised by their ability to reshape raw, stationary materials through the use of a cutting tool that rotates. They help to produce peripheral milled features (such as deeper cavities, threads and slots), face-milled features (such as flat surfaces and shallow cavities) and a variety of other shapes.
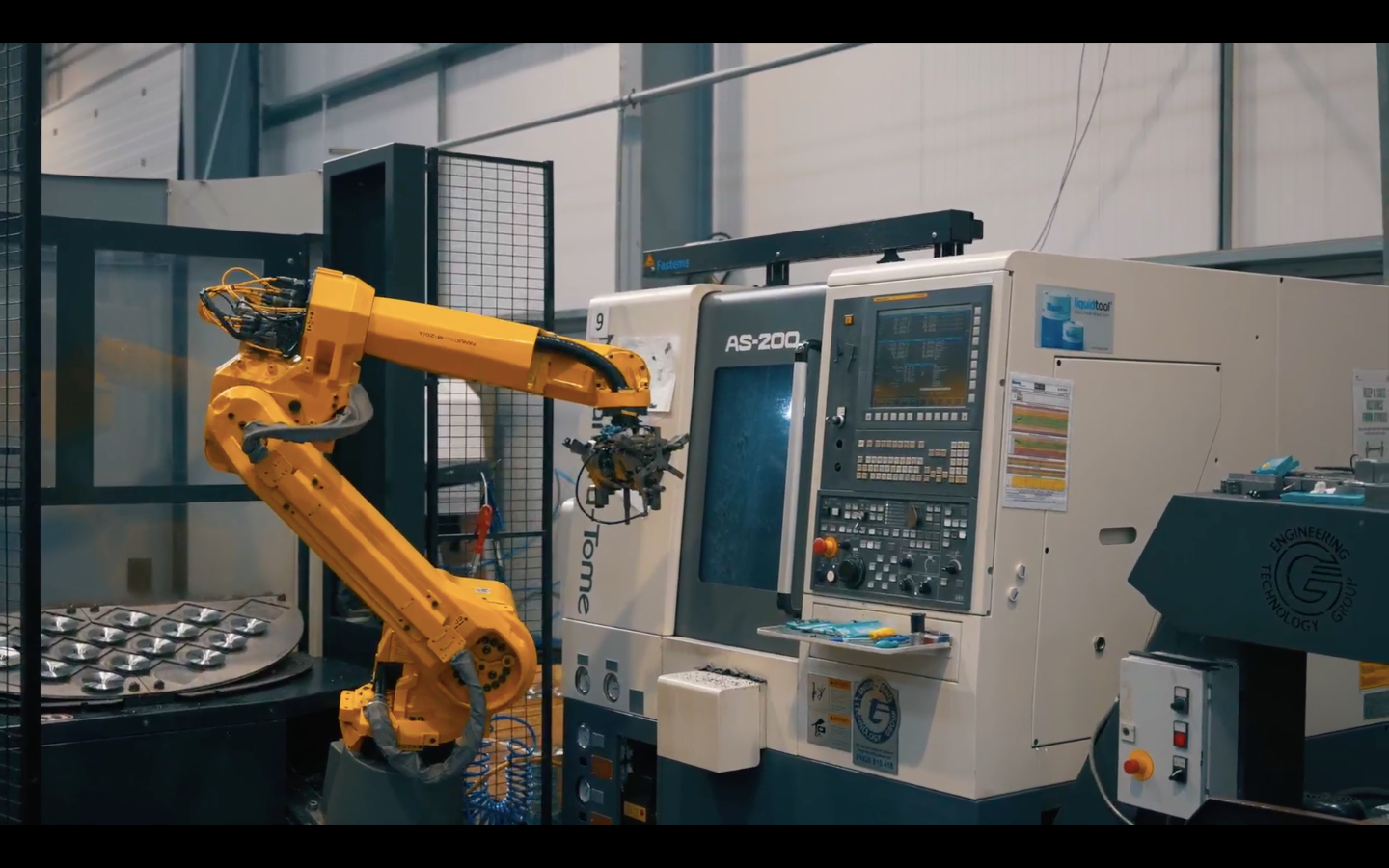
CNC lathes and turning machines – These can rotate or turn raw materials during the cutting process, as the cutting tools remain stationary instead. The cutting tools are in linear motions along the turning bar stock, removing materials around the circumference. CNC Swiss lathes are a type of CNC lathe, offering better support to the workpiece as the material is shaped, providing tighter tolerances. Turning machines create external and internal features, including drilled holes, bores, slots, tapers, threads, broaches, and tappings.
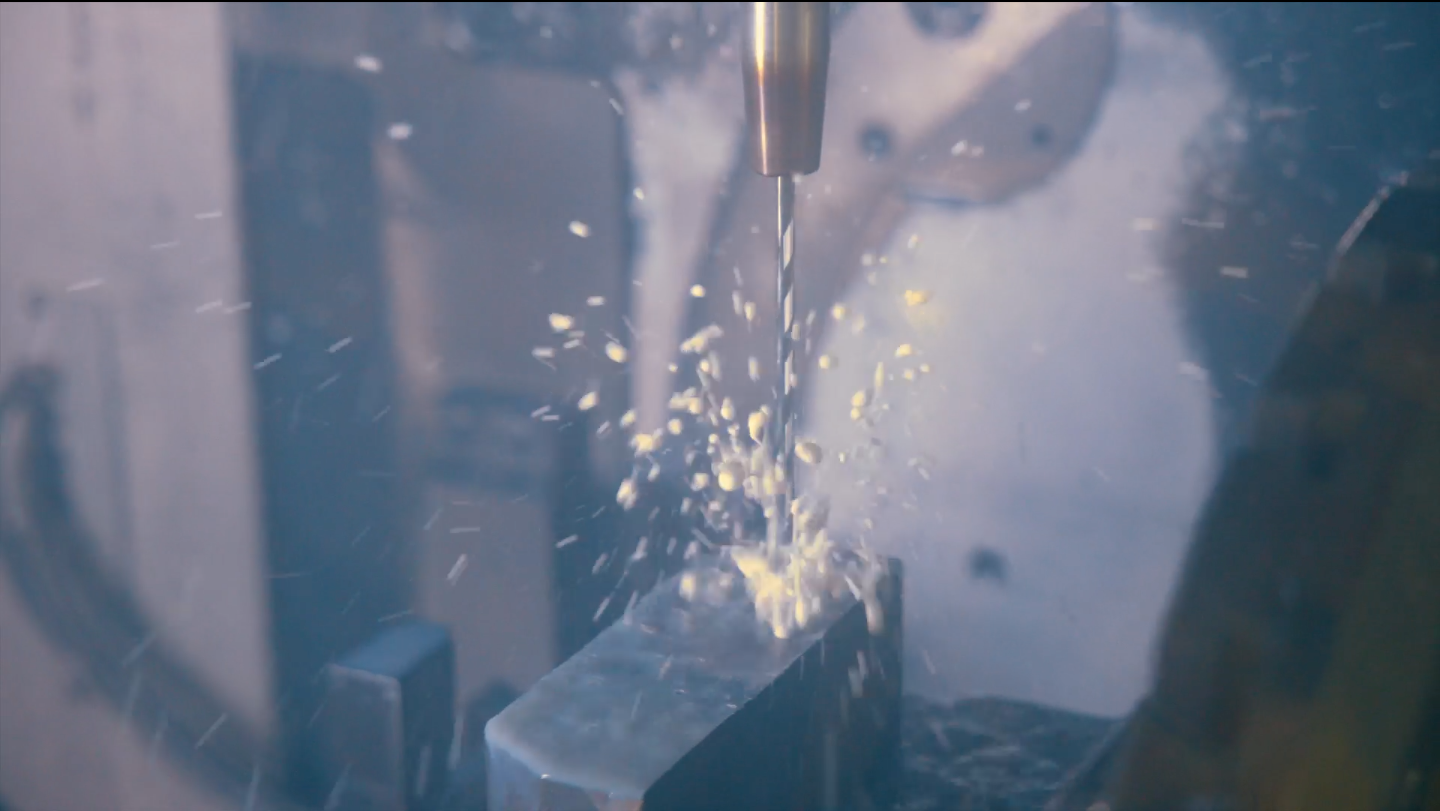
CNC drilling – Drilling is a process within CNC precision machining that utilises rotating drill bits to produce cylindrical holes in the material. Multi-point equipment chips away at the raw material, ensuring advanced hole machining. Examples include spotting drills (for shallow or pilot holes), screw machine drills (for holes without an initial pilot hole), peck drills (to reduce the number of chips created from the workpiece) and chucking reamers (help to enlarge previous holes).
Electrical discharge machines (EDM) – This machine involves the use of controlled electrical sparks to help shape the raw materials into the required shape. You may also hear this referred to as spark machining, die sinking, wire burning, or spark eroding. The technician places the component under an electrode wire and the machine then emits discharges to produce intense heat that melts the material before flushing with an electrolytic fluid to give the desired shape. EDM produces micro holes, precise slots, angled or tapered features.
CNC plasma cutting – These are tools that use a high-powered, computer-controlled plasma torch. The temperatures can reach up to 50,000 degrees Fahrenheit, easily melting workpieces and creating the necessary cuts in the raw material. Materials such as steek, aluminium, copper, brass, and stainless steel must be used with plasma cutting as they are electrically conducive.
CNC precision grinding – Precision grinders are a necessity where there are smooth surface roughness requirements. It is a crucial tool when creating parts and components that have incredible accurate requirements. CNC mills create the rough surface, for grinders to complete the job with the surface finish.
The advantages of precision CNC machining
There are a few obvious advantages to CNC precision machining.
Accuracy – The machines that are used within this type of manufacturing offer high precision and accuracy over long, repeatable production runs. Programming allows for accurate instructions to be delivered over these long runs, limiting the risks of discrepancies that could be found through human error in the longer, more laborious manual process of manufacturing.
Reliability – The computer-controlled machinery is reliable, meaning less downtime due to human error, equipment failure, or malfunctions. Fewer parts and less downtime mean a much lower need for maintenance and repair, and shorter gaps between production runs. All of these things come together as cost and time savings.
Extensive application range – Compatible with several material types, CNC precision machining has that flexibility that is appealing to businesses of difference sizes, as you can work with different types of materials, different tolerances, and for several industry types. Materials include a whole host of metals and plastics
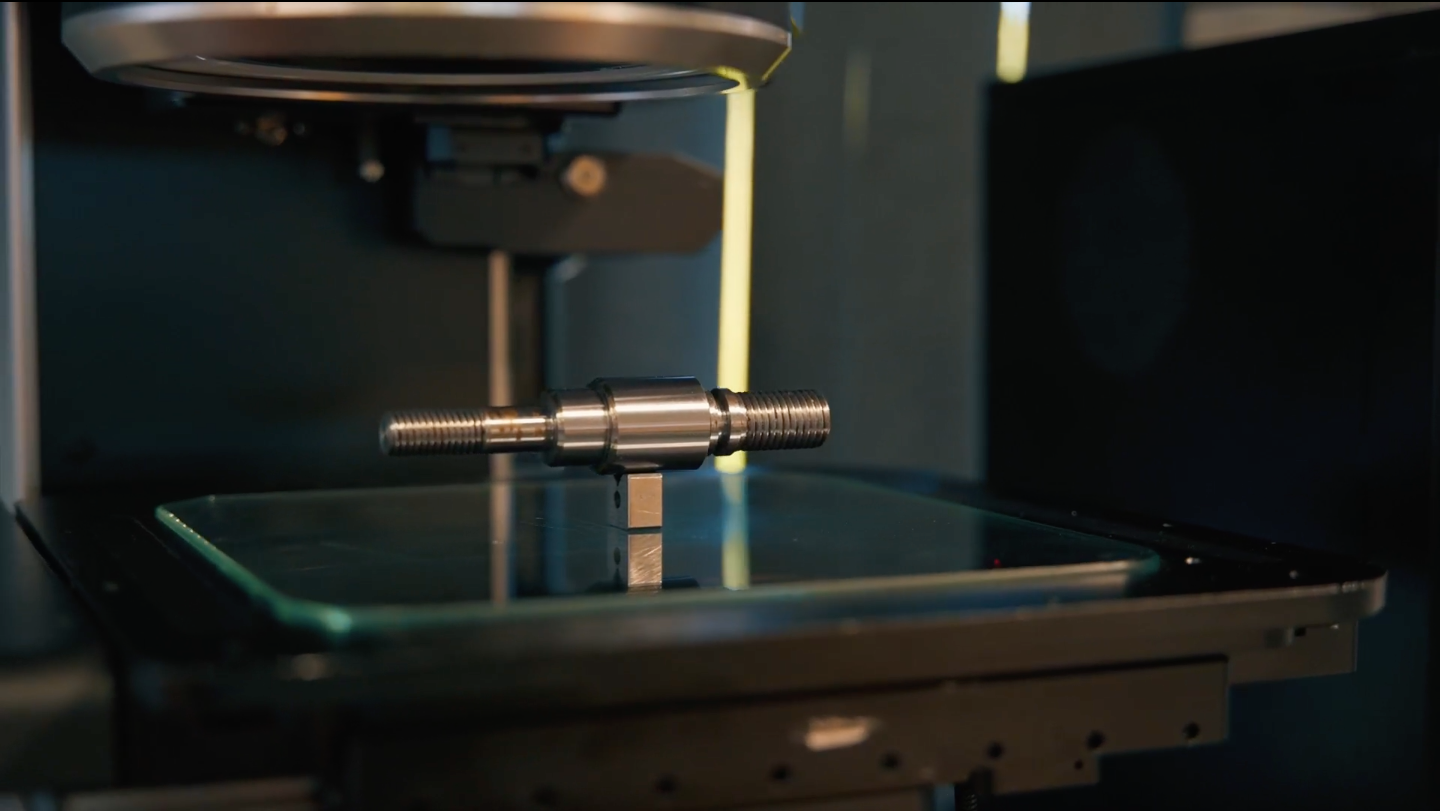
What is the tolerance of CNC precision machining?
When choosing a manufacturing process, tolerance is vital. It defines the acceptable range of variation in a dimension, expressed as a percentage (+/-0.1mm or +/-0.2mm tolerance for instance). The tolerance will depend on the accuracy and size of the part.
Where is CNC precision machining used?
The advantages of CNC precision machining are felt most commonly in the following sectors and industries:
- Automotive industry
- Medical industry
- Aerospace industry
- Military and defence
- Electronics industry
These are all industries where there is a vital need for tight tolerances, reliability, and the latest innovations. Accuracy is vital in all these areas, ensuring that the end product is the same across many thousands of parts and finished product pieces.
CNC precision machining offers efficiency, accuracy, and reliability, helping companies to deliver large production runs with aplomb. This type of manufacturing helps a company to look after its bottom line, to enhance its reputation and to provide the means with which to go on long production runs without worrying of discrepancies from the 1st completed piece to the 1000th.